AP 10th Class Biology 13th Lesson Our Environment Important Questions
Class 10 Biology Chapter 13 Important Questions - 1 Mark
Question 1.
What is an ecosystem?
Answer:
An ecosystem is a geographic area where plants, animals, and other organisms, as well as weather and landscape, work together to form a bubble of life.
Question 2.
What does an ecosystem consist of ?
Answer:
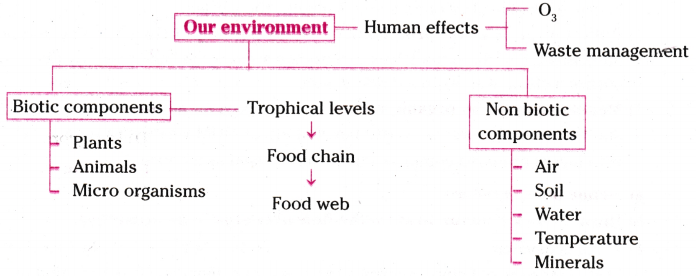
An ecosystem consists of biotic components comprising living organisms and abiotic components comprising physical factors like temperature, rainfall, wind, soil and minerals.
Question 3.
What are the types of ecosystems ?
Answer:
Some ecosystems are formed naturally, forests, ponds and lakes. These are natural ecosystems. While gardens and crop-fields are human made (artificial) ecosystems.
Question 4.
What are the types of organisms in an ecosystem?
Answer:
Organisms can be grouped as producers, consumers and decomposers according to the manner in which they obtain their sustenance from the environment.
Question 5.
Why do we need food?
Answer:
We know that the food we eat acts as a fuel to provide us energy to do work.
Question 6.
Where plants get energy to prepare food ?
Answer:
The autotrophs capture the energy present in sunlight and convert it into chemical energy.
Question 7.
What is a food chain?
Answer:
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms, each dependent on the next as a source of food. It represents the flow of energy and nutrients from one organism to another in an ecosystem.
Question 8.
Define a producer in a food chain.
Answer:
A producer is an organism, usually a plant or algae, that produces its own food through photosynthesis and forms the base of a food chain by providing energy to other organisms.
Question 9.
Give an example of a primary consumer in a food chain.
Answer:
An example of a primary consumer is a herbivore, such as a rabbit, which feeds directly on plants.
Question 10.
Explain the role of decomposers in a food chain.
Answer:
Decomposers, like bacteria and fungi, break down the remains of dead organisms and organic matter, returning nutrients to the soil and completing the cycle of material and energy flow in ecosystems.
Question 11.
Differentiate between a food chain and a food web.
Answer:
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms, while a food web is a complex network of interconnected food chains in an ecosystem, illustrating multiple feeding relationships.
Question 12.
Why are top predators crucial in a food web ?
Answer:
Top predators help regulate the population of lower trophic levels, maintaining the balance of the ecosystem. Their presence influences the abundance and behavior of other species.
Question 13.
What happens to energy as it moves through trophic levels in a food chain ?
Answer:
Energy decreases as it moves through trophic levels in a food chain. Only a portion of the energy is transferred from one level to the next, with the rest lost as heat during metabolic processes.
Question 14.
Provide an example of a detritivore in a food web.
Answer:
An example of a detritivore is a scavenger like a vulture, which feeds on the remains of dead animals.
Question 15.
How does the disruption of one species in a food web affect the entire ecosystem ?
Answer:
The disruption of one species in a food web can have cascading effects, affecting the abundance and behavior of other species and potentially leading to imbalances in the ecosystem.
Question 16.
Name one human activity that can negatively impact food chains and food webs.
Answer:
Deforestation is one human activity that can negatively impact food chains and food webs by destroying habitats and disrupting the balance of ecosystems.
Question 17.
What is the ozone layer ?
Answer:
The ozone layer is a region of Earth’s stratosphere that contains a high concentration of ozone O3 molecules.
Question 18.
What is the primary function of the ozone layer ?
Answer:
The primary function of the ozone layer is to absorb and block the majority of the sun’s harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
Question 19.
What is the main cause of ozone layer depletion ?
Answer:
The main cause of ozone layer depletion is the release of man-made chemicals called ozone-depleting substances (ODS), such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and halons.
Question 20.
How does ozone depletion affect living organisms ?
Answer:
Ozone depletion allows more UV radiation to reach the Earth’s surface, which can lead to various health issues in humans, such as skin cancer and cataracts. It can also harm ecosystems and marine life.
Question 21.
Which international agreement aims to protect the ozone layer ?
Answer:
The Montreal Protocol is an international treaty designed to phase out the production and consumption of ozone-depleting substances to protect the ozone layer.
Question 22.
What are the natural sources of ozone in the atmosphere?
Answer:
Lightning and certain natural processes release small amounts of ozone into the atmosphere, contributing to the presence of ozone in the stratosphere.
Question 23.
Name one positive effect of the ozone layer.
Answer:
One positive effect of the ozone layer is its role in blocking harmful UV-B and UV-C radiation, which is crucial for protecting life on Earth.
Question 24.
How does ozone layer depletion lead to the formation of the ozone hole ?
Answer:
Ozone layer depletion, particularly over Antarctica, leads to the formation of the ozone hole due to the destruction of ozone molecules by human-made chemicals, creating a region with significantly reduced ozone concentrations.
Question 25.
Which UV radiation does the ozone layer primarily absorb ?
Answer:
The ozone layer primarily absorbs UV-B and UV-C radiation, preventing them from reaching the Earth’s surface.
Question 26.
How can individuals contribute to the protection of the ozone layer?
Answer:
Individuals can contribute to the protection of the ozone layer by using ozone-friendly products, such as those labeled "ozone-friendly" or "CFC-free," and by, adopting environmentally responsible practices to reduce the use of ozone-depleting substances.
Question 27.
Will the natural replenishment of the soil take place, even if decomposers are not there?
Answer:
No it’s not possible the natural replenishment of the soil take place, even if decomposers are not there.
Question 28.
We generate a lot of material that is thrown away, What are some of these waste materials ?
Answer:
Items often included in this category include product packaging, yard waste, clothing, food scraps, appliances, paints, and batteries.
Question 29.
Have you ever wondered why the same enzyme does not break-down everything we eat?
Answer:
Enzymes are specific in their action, specific enzymes are needed for the break-down of a particular substance. That is why we will not get any energy if we try to eat coal
Question 30.
What do you think are the advantages of disposable paper-cups over disposable plastic cups?
Answer:
Disposable paper cups are easily decomposed by microorganisms. Hence they create lesser pollution issues and can be easily buried as compost or can be easily burned causing less pollution compared to disposable plastic cups.
Question 31.
Study the given figure of a Food web and write the primary consumer in the food web:
Answer:
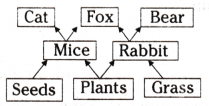
Answer:
Mice and Rabbit.
Question 32.
Assertion : Food chain is responsible for the entry of harmful chemicals in our bodies.
Reason: The length and complexity of food chains vary greatly,
A) Both A and R are true, and R is correct explanation of the assertion.
B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
C) A is true but R is false.
D) A is false but R is true.
Answer:
B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
Question 33.
In 1987, an agreement was formulated by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) to freeze the production of " X " to prevent depletion of " Y " " X " and " Y " respectively referred here are :
A) Ozone; CFCs
B) CFCs; rays UV
C) CFCs; Ozone
D) UV rays Diatomic oxygen
Answer:
C) CFCs ; Ozone
Question 34.
Which of the following features relates to biodegradable substances ?
A) Broken down by biological processes
B) Remain inert
C) Persist in environment for long time
D) May harm the ecosystem
Answer:
A) Broken down by biological processes
Question 35.
Assertion : Biodegradable substances result in the formation of compost and natural replenishment.
Reason : It is due to breakdown of complex inorganic substances into simple organic substances.
A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C) A is true but R is false.
D) A is false but R is true.
Answer:
C) A is true but R is false.
Question 36.
Create a terrestrial food chain depicting four trophic levels.
Answer:
A terrestrial food chain depicting four trophic levels can be represented as:
Grass → Rabbit → Fox → Lion.
Question 37.
From the following group of organisms create a food chain which is most advantageous for human beings in term of energy?
Hawk, rat, cereal plant, snake, human being
Answer:
Cereal plant → Human being
Question 38.
Mention the percentage of energy available in the organism shown in the flow chart.

Answer:
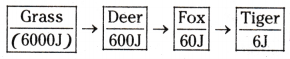
Question 39.
Name the secondary consumer in the following food chain.
Green plants → Grass hopper→ Frog → Snake → Hawk.
Answer:
Frog is the secondary consumer.
Question 40.
Name the primary consumer in the above Trophic level.
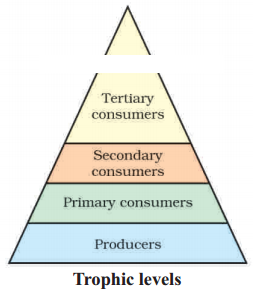
Answer:
Grass hopper / Rabbit / Goat is the primary consumer in the above Trophic level.
Question 41.
In which do we find much accumulation of pollutants in these trophic levels?
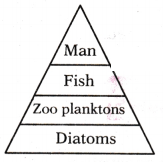
Answer:
We find much accumulation of pollutants in Zoo planktons.
Question 42.
What is the secondary consumer in this food chain?

Answer:
Frog
Question 43.
What are the secondary consumers in the adjacent diagram?
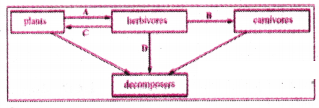
Answer:
Carnivores.
Question 44.
How many oxygen molecules present in Ozone?
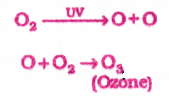
Answer:
Three
Question 45.
Draw a food chain.
Answer:

Question 46.
Fill the food chain.
grass →.... → tiger
Answer:
deer.
Question 47.
What is the role of the ozone layer?
Answer:
The ozone layer in the stratosphere absorbs a portion of the radiation from the sun, preventing it from reaching the planet’s surface.
Question 48.
Why should we protect plants?
Answer:
Plants and animals hold medicinal, agricultural, ecological, commercial and aesthetic value. So, they must be protected.
Question 49.
What is 3R ?
Answer:
The 3R’s are used to refer to the three terms that are : Reduce, Reuse and Recycle.
Our Environment Class 10 Important Questions - 2 Marks
Question 1.
Is the garden an ecosystem?
Answer:
Yes, if we visit a garden we will find different plants, such as grasses, trees; flower bearing plants like rose, jasmine, and sunflower; and animals like frogs, insects and birds. All these living organisms interact with each other and their growth, reproduction and other activities are affected by the abiotic components of the ecosystem. So a garden is an ecosystem.
Question 2.
What are producers?
Answer:
Which organisms can make organic compounds like sugar and starch from inorganic substances using the radiant energy of the Sun in the presence of chlorophyll? All green plants and certain bacteria which can produce food by photosynthesis come under this category and are called the producers.
Question 3.
What are consumers ?
Answer:
Organisms depend on the producers either directly or indirectly for their sustenance, These organisms which consume the food produced, either directly from producers or indirectly by feeding on other consumers are the consumers. Consumers can be classed variously as herbivores, carnivores, omnivores and parasites.
Question 4.
How did the food web form?
Answer:
The length and complexity of food chains vary greatly. Each organism is generally eaten by two or more other kinds of organisms which in turn are eaten by several other organisms. So instead of a straight line food chain, the relationship can be shown as a series of branching lines called a food web.
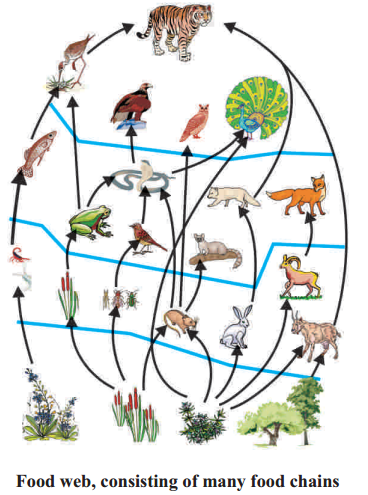
Question 5.
Define a Food Chain.
Answer:
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms, where each member represents a link in the transfer of energy and nutrients. It begins with a producer (usually a plant) that synthesizes its own food through photosynthesis, followed by various consumers (animals) that feed on each other, forming a sequential flow of energy.
Question 6.
Explain the importance of decomposers in a food chain.
Answer:
Decomposers play a crucial role in a food chain by breaking down organic matter from dead plants and animals into simpler substances. This process, known as decomposition, releases nutrients back into the environment, making them available for producers to use again. Without decomposers, nutrients would be locked in dead organic matter, hindering the recycling of materials and the sustainability of the ecosystem.
Question 7.
Differentiate between a Food Chain and a Food Web.
Answer:
A food chain is a linear representation of the flow of energy and nutrients, illustrating a single pathway of consumption in an ecosystem. In contrast, a food web is a more complex and interconnected system that depicts multiple overlapping food chains within an ecosystem.
While a food chain follows a straight line, a food web demonstrates the intricate relationships between various organisms in an ecosystem, highlighting the multiple paths through which energy and nutrients can flow.
Question 8.
Describe the role of producers in a food chain.
Answer:
Producers, often plants, are the foundation of a food chain. They play a crucial role by converting sunlight into energy through the process of photosynthesis. This energy is then utilized to synthesize organic compounds, providing a source of food for the entire ecosystem. Producers form the initial link in the food chain, and their productivity influences the abundance and health of the entire ecosystem.
Question 9.
Give an example of a tertiary consumer in a food chain.
Answer:
Tertiary consumer is an organism that occupies the fourth trophic level in a food chain and primarily preys on other consumers. An example of a tertiary consumer is a top predator like a hawk or an apex predator like a lion in a terrestrial ecosystem. These organisms feed on secondary consumers, which, in turn, consume primary consumers, forming a multi-level hierarchy in the food chain.
Question 10.
What is the ozone layer ?
Answer:
The ozone layer is a region of the Earth’s stratosphere that contains a high concentration of ozone (O3) molecules. It plays a crucial role in absorbing the majority of the sun’s harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation, thereby protecting life on Earth.
Question 11.
Why is the ozone layer important for life on Earth ?
Answer:
The ozone layer is essential for life on Earth because it absorbs and blocks a significant portion of the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Excessive UV radiation can cause harmful effects such as skin cancer, cataracts, and damage to ecosystems. The ozone layer acts as a protective shield, preventing these harmful rays from reaching the Earth’s surface and thus safeguarding the health of living organisms.
Question 12.
Why does plastic become a big problem to the environment?
Answer:
- Many human-made materials like plastics will not be broken down by the action of bacteria or other saprophytes.
- These materials will be acted upon by physical processes like heat and pressure, but under the ambient conditions found in our environment, these persist for a long time.
Question 13.
Look at the figure, here are three food chains in which ecosystem you can see these food chains ?

Answer:
Food chain in nature (a) in forest, (b) in grassland and (c) in a pond
Question 14.
Why the number of producers are more in number in a food pyramid ?
Answer:
There are more producers than consumers in an energy pyramid because energy transfer between trophic levels is not 100% efficient. Producers (plants) convert sunlight into biomass through photosynthesis, capturing a portion of the energy.
Question 15.
Imagine the situation where you do not clean the aquarium and some fish and plants have died. Have you ever thought about what happens when an organism dies?
Answer:
- The microorganisms, comprising bacteria and fungi, break-down the dead remains and waste products of organisms.
- These microorganisms are the decomposers as they break-down the complex organic substances into simple inorganic substances that go into the soil and are used up once more by the plants.
Question 16.
What will happen to the garbage, and dead animals and plants in decomposers absence?
Answer:
- If all the decomposers are eliminated it will cause piling up of excretions, dead bodies of various plants and animals, and litter.
- This will lead to a shortage of free space as there will be numerous dead and decaying matter on the Earth.
- So much nitrogen would be locked up in leaves and other tissues that there would not be enough nitrogen available for the plant to make new leaves, stems and wood.
Question 17.
What happens after we throw them away?
Answer:
- Our environment become dirty and unclean.
- It causes health issues.
- Natural resources are spoiled.
- It leads to pollution.
Question 18.
What will be the amount of energy available to the organisms of the 2nd trophic level of a food chain, if the energy available at the first trophic level is 10,000 joules?
Answer:
- According to Lindeman’s 10% law, only 10% of energy is transferred to next level.
- If energy available at first trophic level is 10,000 Joules, then at second trophic level energy available will be 10% of 10,000 which equals to 1000 Joules.
Question 19.
What is meant by garbage ? List two classes into which garbage is classified.
Answer:
Garbage is the household waste or rubbish produced in our day-to-day life.
Ex : Spoilt food, vegetable peels, leaves, wood, grass, paper, plastic, etc.
Garbage is classified into the following two types :
- Biodegradable garbage : Garbage that can be decomposed naturally.
Ex : vegetable peels, leaves, paper, etc.
- Non-Biodegradable garbage : Garbage that cannot be decomposed naturally.
Ex : metal, plastics, etc.
Question 20.
In the following food chain, 100J of energy is available to the lion. How much energy was available to the producer?
Plant → Deer → Lion
Answer:
- As per 10% law of flow of energy in an ecosystem only 10% of energy is received by the next trophic level. Hence, in the given food chain:
- If 100 Joules of energy is available to lion, the plants or producers have 10,000 Joules of energy available to them.

Question 21.
Study the food chain given below and answer the questions that follow:
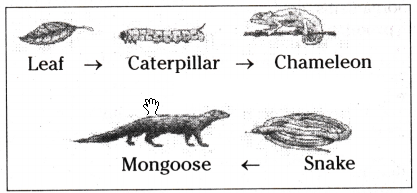
a) If the amount of energy available at the third trophic level is 100 joules, then how much energy will be available at the producer level? Justify your answer.
b) Is it possible to have 2 more trophic levels in this food chain just before the’ fourth trophic level? Justify your answer.
Answer:
a) The producer level has 10000 J because only 10% of energy is available for the next trophic level.
b) No, since the loss of energy at each step is so great that very little usable energy will remain after 4 trophic levels.
Question 22.
The figure given below represents different trophic levels in a food chain. And answer the following questions.
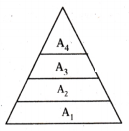
i) Which trophic level has maximum energy ?
Answer: The producers have maximum energy.
ii) Which trophic level has minimum energy?
Answer: The top most trophic level has minimum energy.
Question 23.
If we discontinue the use of plastic, how can an environment-friendly substitute be provided?
Answer:
- Best alternatives can be use of stainless steel, glass and platinum, silicon storage containers.
- Cloth bags can be used in place of plastic bags.
- Use of wooden cleaning brushes, kitchen utensils and cutting board, pottery and other ceramic products etc.
Question 24.
Complete the following table.
|
Oxygen |
Ozone |
| Formula |
(i) |
(ii) |
Benefits to
biotic component |
(iii) |
(iv) |
Answer:
(i) O2
(ii) O2
(iii) Respiration
(iv) Absorbs harmful uv rays coming from the sun.
Question 25.
Grass → Grass hopper → Frog → Snake → Hawk
What will happen if we remove frog from the above food chain?
Answer:
- Frog is secondary consumer in this food chain.
- If we remove frog from the food chain, the number of grasshopper will increase, on other hand the number of snakes which depend on frogs will decrease.
- Hence ecological balance may be damaged.
Question 26.
Observe the different trophic levels pyramid and answer the following questions.

i) As per the number of organisms in the trophic level, which group of organisms are more and which are less in number?
ii) What happens if secondary consumer disappear ?
Answer:
i) If producers are more in number, then tertiary consumers are less in number. If secondary consumers disappear the primary consumers increase in number and the tertiary consumers found no food to live.
ii) It leads to death.
Question 27.
The following organisms form a food chain. Which of these will have the highest concentration of non - biodegradable chemicals? Name the phenomenon assoclated with it.
Insects, Hawk, Grass, Snake, Frog
A.nswer:
Among the organisms of the food chain, hawk being top consumer is present at top most trophic level, hence will have the highest concentration of non - biodegradable chemicals due to a phenomenon known as bio magnification.
Question 28.
Differentiate the bio accumulation and biological magnification.
Answer:
| Bio Accumulation |
Bio Magnification |
| The process of entry of pollutants into a food chain is known as bio accumulation. |
It is the tendency of pollutants to concentrate as they move from one trophic level to the next is known as Bio magnification. |
Important Questions on Our Environment Class 10 - 4 Marks
Question 1.
How the energy is transferred in the food chain ?
Answer:
- Each step or level of the food chain forms a trophic level.
- The autotrophs or the producers are at the first trophic level. They fix up the solar energy and make it available for heterotrophs or the consumers.
- The herbivores or the primary consumers come at the second.
- Small carnivores or the secondary consumers at the third and larger carnivores or the tertiary consumers form the fourth trophic level.

Question 2.
Flow of energy in the food chain is unidirectional. Do you agree to this ?
Answer:
- The flow of energy is unidirectional in food chain or an ecosystem.
- The energy that is captured by the autotrophs does not revert back to the solar input and the energy which passes to the herbivores does not come back to autotrophs.
- As it moves progressively through the various trophic levels it is no longer available to the previous level.
- Secondly, the energy available at each trophic level gets diminished progressively due to loss of energy at each level.
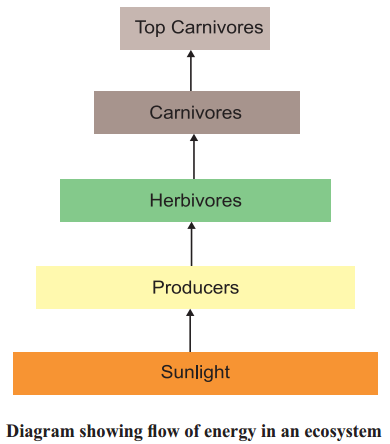
Question 3.
How harmful chemicals enter into the food chain ?
Answer:
- Some harmful chemicals enter our bodies through the food chain.
- One of the reasons is the use of several pesticides and other chemicals to protect our crops from diseases and pests.
- These chemicals are either washed down into the soil or into the water bodies.
- From the soil, these are absorbed by the plants along with water and minerals, and from the water bodies these are taken up by aquatic plants and animals. This is one of the ways in which they enter the food chain.
Question 4.
Why our food grains such as wheat and rice, vegetables and fruits, and even meat, contain varying amounts of pesticide residues.
Answer:
- Chemicals that enter into the food chain are not degradable, these get accumulated progressively at each trophic level.
- As human beings occupy the top level in any food chain, the maximum concentration of these chemicals get accumulated in our bodies. This phenomenon is known as biological magnification.
- This is the reason why our food grains such as wheat and rice, vegetables and fruits, and even meat, contain varying amounts of pesticide residues.
- They cannot always be removed by washing or other means.
Question 5.
Observe the figure (fig 13.3) and answer the following questions.

a) Write any two food chains from the figure.
b) What are the producers in the above diagram ?
c) Which one is the top consumer?
d) What are the secondary consumers in the figure?
Answer:
a)
- grass → rabbit → fox → tiger.
- grass → rat → snake → eagle
b) grass, trees
c) tiger
d) fox, frog, snake
Question 6.
What are the bio-degradable and non-biodegradable materials ?
Answer:
bio-degradabie substances : Such substances which can be easily broken down by the action of bacteria are named bio-degradable substances.
Non-bio-degradable substances: Other substances or materials like plastics, metallic cans and pesticides which cannot be broken down easily by biological processes are named non-bio-degradable substances.
Question 7.
Explain the concept of a food chain and provide an example.
Answer:
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms, where each organism serves as a source of food for the; next in the sequence. It represents the flow of energy and nutrients in an ecosystem.
Example : Grass → Rabbit Fox
In this example, grass is the producer, the rabbit is the primary consumer, and the fox is the secondary consumer. The arrow indicates the direction of energy transfer, as each organism gets its energy by consuming the organism before it in the chain.
Question 8.
Define a food web and describe its importance in an ecosystem.
Answer:
A food web is a complex network of interconnected food chains that represents the feeding relationships within an ecosystem. Unlike a linear food chain, a food web accounts for the multiple interactions and connections between various species.
Importance :
Biodiversity: Food webs highlight the diversity of species in an ecosystem, showcasing the interconnectedness of different organisms.
Stability : The complexity of a food web contributes to the stability of an ecosystem. If one species is affected, it may have cascading effects on other species, influencing the overall balance.
Energy Flow : Food webs provide a more realistic depiction of energy flow in ecosystems, as many organisms have multiple sources of food and can be part of different trophic levels.
Adaptations : Organisms in a food web often develop specific adaptations based on their role and interactions. This leads to the evolution of diverse traits and behaviors within the ecosystem.
Question 9.
Discuss the impact of human activities on food chains in an ecosystem.
Answer:
Human activities can significantly impact food chains in ecosystems, often leading to disruptions and imbalances.
Habitat Destruction : Deforestation and urbanization can destroy habitats, disrupting the natural habitats of various species and affecting their roles in food chairs.
Pollution : Industrial and agricultural pollutants can contaminate ecosystems, affecting the health of organisms and the quality of their food sources.
Overharvesting : Overfishing and overhunting can lead to the depletion of certain species, affecting both their population size and the organisms that depend on them for food.
Introduction of Invasive
Species : Human activities can introduce non-native species into ecosystems, leading to competition for resources and potentially causing the decline or extinction of native species.
Question 10.
Explain the difference between a producer and a decomposer in a food chain. Provide examples of each.
Answer:
Producers and decomposers play crucial roles in a food chain.
Producers: These are organisms that produce their own food through photosynthesis. They form the base of the food chain, converting sunlight into energy.
Example : Plants algae
Decomposers: Decomposers break down organic matter, releasing nutrients back into the ecosystem. They play a vital role in recycling dead organisms and organic material.
Example : Bacteria, fungi
While producers initiate the food chain by producing their own food, decomposers contribute to the cycle by breaking down and recycling organic material, ensuring the sustainability of the ecosystem.
Question 11.
Why is the ozone layer important ?
Answer:
The ozone layer is important because it acts as a shield against the harmful effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. UV radiation can cause skin cancer, cataracts, and other health problems in humans, as well as harm ecosystems and wildlife. The ozone layer protects living organisms by absorbing and blocking a significant portion of these harmful rays.
Question 12.
What are ozone-depleting substances (ODS) ?
Answer:
Ozone-depleting substances (ODS) are human-made chemicals that contain chlorine, fluorine, bromine, or carbon, which can contribute to the depletion of the ozone layer. Examples include chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), halons, carbon tetrachloride, and methyl chloroform. These substances release reactive chlorine and bromine atoms into the stratosphere, leading to the breakdown of ozone molecules.
Question 13.
What efforts have been made to protect the ozone layer ?
Answer:
The most significant international effort to protect the ozone layer is the Montreal Protocol, which was adopted in 1987. The protocol aims to phase out the production and consumption of ozone-depleting substances. Since its implementation, there have been significant reductions in the production of ODS, leading to the gradual recovery of the ozone layer. The success of the Montreal Protocol serves as a model for global cooperation in addressing environmental issues.
Question 14.
Draw the diagram of energy flow in an ecosystem.
Question 15.
Consumers can be classified variously as herbivores, carnivores, omnivores and parasites. Can you give examples for each of these categories of consumers ?
Answer:
Herbivores: A herbivore is an organism that mostly feeds on plants.Horse, cow, mule, donkey and buffalo are some domesticated animals that are herbivores.
Carnivores : The word carnivore is derived from Latin and literally means "meat eater." A carnivore is an animal that feeds on other animals hawks and snakes.
Omnivores: An omnivore is an organism that can feed on both plant and animal sources. Example : Dogs, Bears.
Humans : Humans have a wide range of diets, from completely herbivorous to almost entirely carnivorous, but most humans eat some amount of both meat and plants.
Question 16.
Use of several pesticides which results in excessive accumulation of pesticides in rivers or ponds, is a matter of deep concern. Justify this statement.
Answer:
- Several pesticides and other chemicals are used to protect our crops from diseases and pests.
- These chemicals are either washed down into the soil or into the water bodies.
- From the soil, these are absorbed by the plants along with water and minerals, and from the water bodies these are taken up by aquatic plants and animals.
- As these chemicals are not degradable, these get accumulated progressively at each trophic level due to biological magnification.
- Thus, it is extremely concerning when pesticides are used in large quantities that cause an excessive buildup in rivers or ponds.
Question 17
In the following food chain, only 2J of energy was available to the peacocks. How much energy would have been present in Grass ? Justify your answer.
GRASS → GRASSHOPPER → FROG→ SNAKE → PEACOCK
Answer:
Energy that would be present in Grass is 20000J
Justification :
- According to the ten percent law of energy in a food chain, only ten percent of energy is transferred to the next trophic level.
- Thus, the energy keeps on decreasing by 10% at each level.
- If, Energy available to grass = 20000J Energy available to grass hopper = 10% of 20000 = 2000J
- Energy available to frog = 10% of 2000 = 200J
- Energy available to snake = 10% of 200 = 20J
- Energy available to peacock = 10% of 20 = 2J
Question 18.
We often observe domestic waste decomposing in the bylanes of residential colonies. Suggest ways to make people realise that the improper disposal of waste is harmful to the environment.
Answer:
For making the people aware about the proper disposed of waste for the conservation of the environment, these are the ways to be followed :
- Educate the people about disposing waste and tell them the pros and cons.
- Announce and perform the cleanliness drive campaign and tell them to clean their surroundings themselves.
- Awareness campaign of disposing of wet and dry wastes separately, so that it is easy for the ipunicipality to dispose of them properly.Volunteers should do short plays to make people.
- Posters related to the harmful impact of the decomposing household wastes on the by lanes of their residential colonies.
Question 19.
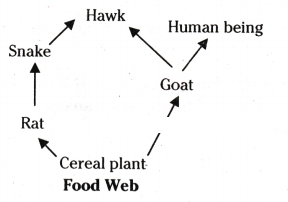
a) From the following group of organisms create a food chain which is the most
advantageous for Human beings in terms of energy.
Hawk, Rat, Cereal plant,
Goat, Snake, Human Being
b) State the possible disadvantage if the cereal plant is growing in soil rich in pesticides.
c) Construct a food web using the organisms mentioned above.
Answer:
a) The most advantageous food chain to Humans is Cereal plant → Goat → Human being. Since this food chain has least number of trophic levels, it we more advantageous to the Human beings in terms of energy.
b) The major disadvantage of growing cereals in pesticide rich soil is that it will accumulate chemicals in the successive trophic levels. As the wastes.
c)
Plastic cups were used to serve tea in trains in early days - these could be returned to the vendors, cleaned and reused. Later, Kulhads were used instead of plastic cups. Now, paper cups are used for serving tea. What are the reasons for the shift from Plastic to Kulhads and then finally to paper cups ?
Answer:
- Use of Plastic cups raised the concern towards hygiene, so they were replaced by disposable plastic cups.
- Plastic cups are non-biodegradable and harm the environment friendly. They were thus replaced by Kulhads.
- Making Kulhad made of clay on a large scale resulted in the loss of top fertile soil.
- Now, disposable paper cups are used because as the paper can be recycled, it is biodegradable and is eco-friendly material which does not cause environmental pollution.
Question 21.
The following organisms form a food chain.
Insect, Hawk, Grass, Snake, Frog
Which of these will have highest concentration of non-biodegradable chemicals ? Name the phenomenon.
Answer:
- The food chain is Grass → Insect → Frog → Snake → Hawk
- The highest concentration of non-biodegradable chemicals will be present in Hawk
as it occupies the last trophic level.
- This phenomenon is termed as biomagnification.
- It is defined as the increase in the concentration of pollutants or harmful chemicals with the increase in trophic level.
Question 22.
Human body is made up of five important components, of which water is the main component. Food as well as potable water are essential for every human being. The food is obtained from plants through agriculture, pesticides are being used extensively for a high yield in the fields.
These pesticides are absorbed by the plants from the soil along with water and minerals and from the water bodies these pesticides are taken up by the aquatic animals and plants.
As these chemicals are not biodegradable, they get accumulated progressively at each trophic level. The maximum concentration of these chemicals gets accumulated in our bodies and greatly affects the health of our mind and body.
Questions:
a) Why is the maximum concentration of pesticides found in human beings ?
b) Give one method which could be applied to reduce our intake of pesticides through food to some extent.
c) Various steps in a food chain represent:
a) Food web
b) Trophic level
d) With regard to various food chains operating in an ecosystem, man is a :
a) Consumer
b) Producer
c) Producer and consumer
d) Producer and decomposer
Answer:
a) Maximum concentration of pesticides is found in human beings because humans comprise the topmost level into the food chain. In the process of biological magnification, the concentration of pesticides increases from going bottom to top level organisms.
b) Organic farming should be practiced to reduce the intake of pesticides through food to some extent. In organic farming, chemical pesticides must be replaced with biopesticides.
c) Various steps in a food chain represent: b) Trophic level.
d) With regard to various food chains operating in an ecosystem, man is a: a) Consumer
Question 23.
Observe the following pyramid of biomass and answer the following questions.
a) This pyramid shows a decrease in the biomass as we move up, why the biomasi is decreasing.
Answer:
- The pyramid of biomass for the given food chain at each step 90% of the food is lost.
- That means 1000 kgs of phytoplankton to produce 100 kgs of zoo plankton to form 10 kgs of fish to produce 1 kg of human tissues.
- The fewer the steps in the food chain the more energy will be for the species at the top.
b) Where do producers get the energy from ?
Answer: Producers get energy from the sun.
c) How much biomass is lost at each step ?
Answer: 90% of biomass is lost at each step.
Question 24.
Observe the trophic levels pyramid and answer the following questions.

i) Which trophic level has less number of organisms ?
Answer: Tertiary consumers trophic level has less number of organisms.
ii) Who are the producers in the given pyramid?
Answer: Plants.
iii) Give two examples of primary consumers.
Answer: Insects, Grasshoppers.
iv) What happens if the primary consumers are removed from the pyramid ?
Answer:
If the primary consumers are removed from the pyramid then the producers will increase in number. So secondary & tertiary consumers found no food to live and leads to death.
Question 25.
a) What does a trophic level represent in a food chain ?
b) State the position of autotrophs and herbivores in a food chain.
Answer:
a) Trophic level represents each of several hierarchical levels of a food chain operating in an ecosystem, consisting of organism sharing the same function in the food chain and the same nutritional relationship to the primary sources of energy,
b)
- The position of producers in a food chain constitute the first trophic level.
- They fix up sun’s energy and make it available for consumers.
- The herbivores or primary consumers constitute the second trophic level.
Question 26.
Complete the following flow chart based on ecosystem and its components.
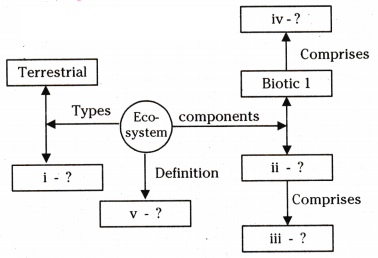
Answer:
- Aquatic
- Abiotic
- Inorganic substances
- Living organisms
- Structural and functional unit of biosphere.
Question 27.
Look at the figure and answer the following questions.
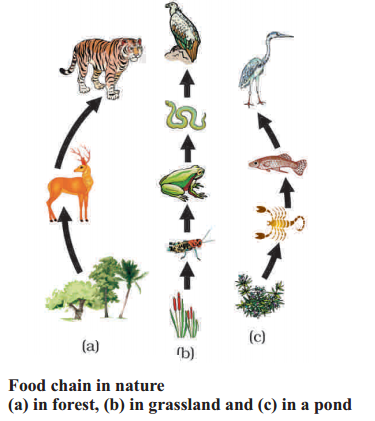
1. What are the producers in the picture ?
Answer: Trees, grass and bushes are producers in this picture.
2. Which food chain has more trophic levels ?
Answer: The middle food chain has more trophic levels.
3. What is the position of frogs in this food chain ?
Answer: Frog has secondary consumer in the food chain.
4. What are the top consumers in this food chain ?
Answer: Tiger, hawk and cranes are top consumers.
Question 28.
Look at the figure and answer the following questions.

1. Give examples for the basic level of the pyramid.
Answer: Basic level of pyramid is producers , green plants are examples for it.
2. Write a suitable food chain for this pyramid.
Answer: Grass → insect → frog → snake.
3. Which level has less number of organisms ?
Answer: Top consumers has less number of organisms.
4. What are the types of consumers ?
Answer: Consumers are three types, those are primary, Secondary and tertiary.
Question 29.
Observe the figure and answer the following questions.

1. What is the food chain ?
Answer: A food chain refers to the order of events in an ecosystem, where one living organism eats another organism.
2. What is the food web ?
Answer: A system of interlocking and interdependent food chains.
3. List out the secondary consumers.
Answer: Fox, fish, frog, snake.
4. What happens if we remove the producers ?
Answer: Food chain is collapsed because lack of food.
Question 30.
Why each organism is important in an ecosystem?
Answer:
- Every little animal within the ecosystem has a vital role in the well-being of the planet.
- If one species is extinct due to some imbalance, it can have significant cascading effects throughout the ecosystem.
- For example, even a small bee is, in fact, a crucial worker in the factory of nature.
- Although each organism’s role is different, all parts of the ecosystem are necessary for the ecosystem to work!
- An organism’s energy role is determined by how it obtains energy and how it interacts with other organisms within the ecosystem.
- The energy roles within an ecosystem are producer, consumer, and decomposer.
Question 31.
What precautions do you take to protect the ozone layer ?
Answer:
- Buy air-conditioning and refrigeration equipment that do not use HCFC’s as refrigerants.
- Buy aerosol products that do not use HCFCs or CFCs as propellants.
- Conduct regular inspection and maintenance of air-conditioning and refrigeration appliances to prevent and minimize refrigerant leakage.
- Avoid the consumption of gasses dangerous to the ozone layer, due to their content or manufacturing process.
- Minimize the use of cars.
- Do not use cleaning products that are harmful to the environment and to us.
- Buy local products.
Extra Questions on Our Environment Class 10 - 8 Marks
Question 1.
What is the food chain ? Explain with a suitable example.
Answer:
Food chain: The sequence of living organisms in a community in which one organism consumes another organism to transfer food energy is called a food chain.
An example of a simple food chain is that operating in a grassland :
Grass (Producer) → Deer (Herbivore) → Lion(Carnivore)
The typical components of a food chain include producers, consumers and decomposers.
Producers (Autotrophs) : These are organisms that produce their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. They are usually plants or algae that convert sunlight into energy. The primary energy source for most ecosystems is sunlight.
Example: Grass is a producer because it uses sunlight to produce its own food through photosynthesis.
Primary Consumers (Herbivores): These are organisms that feed directly on producers. They are herbivores that consume plants for energy.
Example : A rabbit is a primary consumer because it eats grass.
Secondary Consumers (Carnivores or Omnivores): These organisms eat primary consumers. They are carnivores if they consume only meat, and omnivores if they eat both plants and animals.
Example : A fox is a secondary consumer because it eats rabbits.
Tertiary Consumers (Carnivore or Omnivore) : These organisms feed on secondary consumers.
Example : A wolf is a tertiary consumer if it preys on foxes.
Quaternary Consumers (Carnivores or Omnivores) : These consumers eat tertiary consumers.
Example : A mountain lion is a quaternary consumer if it preys on wolves.
Decomposers : These organisms break down the remains of dead plants and animals into simpler substances, returning nutrients to the soil. Decomposers include bacteria and fungi.
Example : Bacteria and fungi decompose the remains of dead plants and animals, releasing nutrients that can be used by producers.


Question 2.
"When one form of energy is changed to another, some energy is lost to the environment in forms which cannot be used again" support this statement.
Answer:
1. The flow of energy between various components of the environment has been extensively studied and it has been found that
2. The green plants in a terrestrial ecosystem capture about 1 % of the energy of sunlight that falls on their leaves and convert it into food energy.
3. When green plants are eaten by primary consumers, a great deal of energy is lost as heat to the environment, some amount goes into digestion and in doing work and the rest goes towards growth and reproduction. An average of 10% of the food eaten is turned into its own body and made available for the next level of consumers.
4. Therefore, 10% can be taken as the average value for the amount of organic matter that is present at each step and reaches the next level of consumers.
5. Since so little energy is available for the next level of consumers, food chains generally consist of only three or four steps. The loss of energy at each step is so great that very little usable energy remains after four trophic levels.
6. There are generally a greater number of individuals at the lower trophic levels of an ecosystem, the greatest number is of the producers.
Question 3.
What is Ozone Layer ? And how it is getting depleted ?
Answer:
1. Ozone (O3) is a molecule formed by three atoms of oxygen. While O2, which we normally refer to as oxygen, is essential for all aerobic forms of life.
2. Ozone is a deadly poison. However, at the higher levels of the atmosphere, ozone performs an essential function.
3. It shields the surface of the earth from ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun. This radiation is highly damaging to organisms, for example, it is known to cause skin cancer in human beings.
4. Ozone at the higher levels of the atmosphere is a product of UV radiation acting on oxygen (O2) molecules. The higher energy UV radiations split apart some molecular oxygen (O2) into free oxygen (O) atoms.
5. These atoms then combine with the molecular oxygen to form ozone as shown.
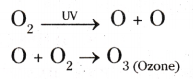
6. The amount of ozone in the atmosphere began to drop sharply in the 1980s. This decrease has been linked to synthetic chemicals like chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) which are used as refrigerants and in fire extinguishers.
7. In 1987, the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) succeeded in forging an agreement to freeze CFC production at 1986 levels.
8. It is now mandatory for all the manufacturing companies to make CFC-free refrigerators throughout the world.
Question 4.
"Our food grains such as wheat and rice, the vegetables and fruits and even meat are found to contain varying amounts of pesticide residues". State the reason to explain how and why it happens.
Answer:
- Pesticides are poisonous chemical substances which are sprayed over crop plants to protect them from pests and diseases.
- These chemical pesticides mix up with soil and water.
- From soil and water, these pesticides are absorbed by the growing plants along with water and other minerals.
- When herbivorous animals feed on these plants the poisonous pesticides enter their bodies through the food chain.
- Similarly, when the carnivorous animals eat these herbivores, the pesticides get transferred to their bodies.
- Therefore, the plant products such as food grains, vegetables and fruits as well as meat of animals contain varying amounts of pesticide residues in them depending upon the trophic level, they occupy in food chain.
Question 5.
Give reason to justify the following :
a) The existence of decomposers is essential in a biosphere.
b) Flow of energy in a food chain is unidirectional.
Answer:
a)
- Decomposers are organisms which survive on the decaying and dead organic matter.
- Decomposers carry out the recycling of nutrients. This helps in releasing the nutrients back into their original pool.
- The carbon from the dead animal will be sent back to air in simpler forms like carbondioxide.
- The decomposing microorganism degrades the garbage that otherwise might become a breeding ground for the germs.
- The dead organisms will stay as they are in the absence of the decomposers.
b)
- The flow of energy in food chain in unidirectional because the sun is the only
source of energy for all ecosystems on earth.
- Then the energy is captured by the autotrophs does not revert back to the sun.
- Therefore, in the food chain, the energy moves progressively through various trophic levels and no longer available to the previous trophic levels.
Question 6.
Write any three characteristics of a food chain. Dharmesh always treated the chemical
effluent before disposing it in the water body. Mention any three moral values possessed by Dharmesh.
Answer:
Characteristics of a food chain :
- A food chain is always straight and proceeds in a progressive straight line.
- A food chain helps in understanding the food relationship and interactions among various organisms in an ecosystem.
- It also helps to understand the movement of toxic substances in an ecosystem and the problem of their biological magnification.
Moral values possessed by Dharmesh :
- Sensitive towards environment.
- Possesses knowledge about biological magnification.
- Scientific temperament.
- Conscious.
Question 7.
"Improvements in our lifestyle have resulted in greater amounts of waste generation." Give two examples to support the given statement. Suggest one change that we can incorporate in our lifestyle in order to reduce non-biodegradable waste.
Answer:
- The improvement in our lifestyle have led to greater amounts of waste generation.
- Recently, there is an increased use of disposable materials like cups, plates, spoons etc in marriages and parties.
- These are usually made up of non-biodegradable substances like plastic and Styrofoam which eventually result in polluting our environment.
- Another example is the use of disposable plastic cups in trains. These leads to generation of a lot of plastic waste.
- However, they are being slowly replaced by paper cups to reduce the burden on the environment.
- We should try to minimise the use of disposable or one time use products in our daily life’s.
- Re-use of plastic containers, polythene bags can reduce the non-biodegradable wastes. Instead, jute bags or paper bags can be used instead of the polythene bags.
Student in a school listened to the news read in the morning assembly that the mountain of garbage in Delhi, suddenly exploded and various vehicles got buried under it. Several people were also injured and there was traffic jam all around.
In the brain storming session the teacher also discussed this issue and asked the students to find out a solution to the problem of garbage. Finally they arrived at two main points - one is self management of the garbage we produce and the second is to generate less garbage at individual level.
Questions:
a) Suggest two measures to manage the garbage we produce.
b) As an individual, what can we do to generate the least garbage ? Give two points.
c) List two values the teacher instilled in his students in this episode.
Answer:
a) The measures that can be undertaken to manage the garbage we produce are :
- Sorting of waste materials as biodegradable and non-biodegradable can help in reducing the menace of waste management. Biodegradable materials can be used for making’ compost, manure etc. while non-biodegradable materials may be used in other forms or recycled.
- One should follow the principle of 3 R’s, which is Reduce, Reuse and Recycle. All the non-biodegradable products that we use should pass through these three stages and only then should go into waste.
b) As an individual we can help in solving this problem with the help of following
steps:
- Use of plastic in any form should be discouraged. For example, disposable products like plastic cups, cans, plastic bags, etc. should be used minimally.
- Most of the kitchen waste can be used for making compost that can be used in potted plants and fields for increasing the soil fertility.
c)
- The teacher instilled a sense of responsibility towards the environment in the students.
- He also made them aware of how we can handle any environmental issue at an individual as well as community level.
Question 9.
Explain in brief about the alternate methods to be followed to prevent the harmful effects such as biological magnification due to over usage of pesticides.
Answer:
Some of alternative pest control methods are :
- Rotation of crops :Growing different crops on a particular piece of land in successive years.
- Studying the life histories of the pests : When this is done it is some times possible to sow the crops at a time when least damage will be caused.
- Biological control: Introducing natural predator or parasite of the pest.
- Sterility : Rendering the males of a pest species sterile.
- Genetic strains : The development of genetic strains which are resistant to certain pest.
- Environmental ethics : People need to know besides laws regarding environment, there are some basic ethics what is right and what is wrong in view of environment.
Question 10.
"All the energy in the ecosystem is ultimately derived from sunlight" - Justify.
Answer:
- All the organisms in an ecosystem derive energy from food.
- In an ecosystem, all the consumers at any level depend upon producers for their food either directly or indirectly.
- The producers in any ecosystem are nothing but photosynthetic organisms such as plants, phyto planktons and photosynthetic bacteria.
- Energy enters the producers in the ecosystem from the sun in the form of solar energy during photosynthesis.
- From the producers, the chemical energy passes to the consumers from one trophic level to the next through food.
- For example, in a grass land ecosystem, grass traps the solar energy and stores in the body.
- When this grass is eaten and assimilated by insects this stored energy enters into the body of insects.
- From the insects, it will pass to frog, from them to snake and soon to eagle.
- Thus, all the energy in the ecosystem is ultimately derived from sunlight.
Question 11.
What is biological magnification ? Will the levels of this magnification be different
at different levels of the ecosystem ?
Answer:
- The tendency of pollutants to concentrate as they move from one trophic level to the next trophic levels is known as Bio magnification.
- Plants absorb pesticides, heavy metals from the soil.
- The primary consumers when eat these plants the remaining of pesticides and heavy metals enter their bodies.
- All these chemicals are not degradable, they accumulate in the bodies of organisms of all trophic levels in the food chain.
- Most of the plants products which we eat are grown in the fields in which pesticides and fertilisers have been used.
- These are absorbed by the plants and cannot be removed by washing or other means.
- Human beings are at the top level of food chain these chemicals get accumulated in our bodies and cause various diseases.
- Levels of biological magnification would increase as the trophic level increases.
Question 12.
Will the impact of removing all the organisms in a trophic level be different for different trophic levels ? Can the organisms of any trophic level be removed without causing any damage to the ecosystem ?
Answer:
- If we remove producers from ecosystem, herbivores will not survive and the entire ecosystem collapse.
- Removing herbivores result in increase the number of producers and carnivores would not get food.
- Removing carnivores result in increase of herbivores to unsustainable levels.
- If we remove decomposers from ecosystem waste material and animal dead remains would pile up and nutrients would not be available to the producers.
- Some or the other damage would be caused to the ecosystem of the organisms of any trophic level is removed.
- However impact of removing producers or decomposers would be serve as the whole ecosystem would collapse.
- Without plants sun’s energy cannot be converted to chemical energy which is the basis of life on the earth.
- Without decomposers the nutrients cannot be replenished and made available to producers.
Question 13.
Write some friendly ecosystem activities you will conduct in your school ?
Answer:
1. Forming eco - clubs: These clubs comprises of student representatives from each class. They will take up the ecofriendly activities and encourage the people of that village to follow environment friendly activities.
2. Setting up garden at school: This ensures the school and its premises green through planting of flowering plants, vegetables and fruit trees. It is a symbol of biodiversity because various plants and animals inhabit the garden.
3. Pollution prevention programme : "A no burning of trash" policy should be implemented in the school. Waste materials are recycled and properly disposed to ensure a clean, waste - free environment.
4. Making compost by organic wastes : By digging a pit at one corner of the school and throwing the organic waste particularly of MDM waste into pit and covering with layers prepares compost which can be used as manure.
Question 14.
a) Define an ecosystem.
b) Draw a block diagram to show the flow of energy in an ecosystem.
Answer:
a)
- An ecosystem is defined as a structural and functional unit of the biosphere.
- It comprises of living organisms and their non - living environment that interact by means of food chains and bio geo chemical cycles resulting in energy flow biotic diversity and material cycling to form stable self supporting system.
b)
- Green plants capture about 1% of the solar energy incident on the earth to carry out the process of photosynthesis.
- A part of this trapped energy is used by plants in performing their metabolic activities and some energy is released as heat into the atmosphere.
- The remaining energy is chemical energy stored in the plants as photosynthetic products.
- When these green plants are eaten up by herbivores, the chemical energy stored in the plants is transferred to these animals.
- These animals utilise some of this energy for metabolic activities and some energy is released as heat while the remaining energy is stored in the body.
- This process of energy transfer is repeated till top carnivores.
- In an ecosystem, transfer of energy follows 10 percent law, i.e., only 10 percent of the energy is transferred to each trophic level from the lower trophic level.
- Nearly 90% of energy is lost when it moves from one trophic level to another.

Conceptual Map: